Linux chmod命令--控制用户对文件的权限
Linux chmod(英文全拼:change mode)命令是控制用户对文件的权限的命令
Linux/Unix 的文件调用权限分为三级 : 文件所有者(Owner)、用户组(Group)、其它用户(Other Users)。
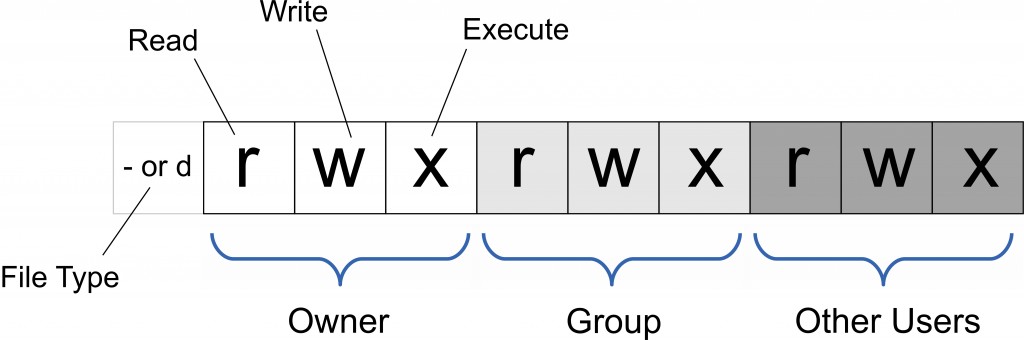
只有文件所有者和超级用户可以修改文件或目录的权限。可以使用绝对模式(八进制数字模式),符号模式指定文件的权限。
安装APPImage结尾的文件,环境:source ~/env_file , 修改权限:chomd +x Ink.. , 使用:./Ink...

将文件 file1.txt 设为所有人皆可读取 :
chmod ugo+r file1.txt将文件 file1.txt 设为所有人皆可读取 :
chmod a+r file1.txt将文件 file1.txt 与 file2.txt 设为该文件拥有者,与其所属同一个群体者可写入,但其他以外的人则不可写入 :
chmod ug+w,o-w file1.txt file2.txt为 ex1.py 文件拥有者增加可执行权限:
chmod u+x ex1.py将目前目录下的所有文件与子目录皆设为任何人可读取 :
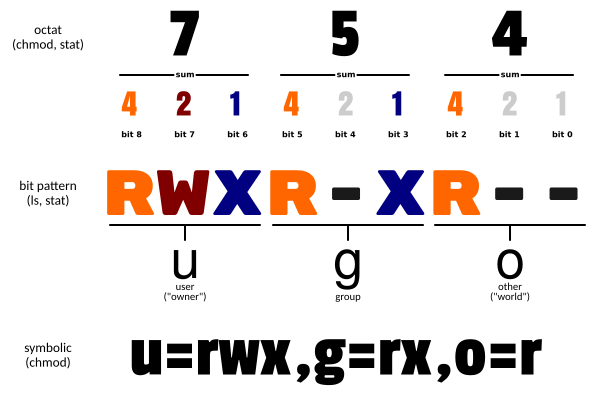
chmod -R a+r *此外chmod也可以用数字来表示权限如 :
chmod 777 file语法为:
chmod abc file其中a,b,c各为一个数字,分别表示User、Group、及Other的权限。
r=4,w=2,x=1
- 若要 rwx 属性则 4+2+1=7;
- 若要 rw- 属性则 4+2=6;
- 若要 r-x 属性则 4+1=5。
chmod a=rwx file和
chmod 777 file效果相同
chmod ug=rwx,o=x file和
chmod 771 file